Spatial Disorientation
ETC's suite of spatial disorientation trainers optimize the elements of simulation fidelity including cockpit, visuals, flight model, and vestibular stimulation through continuous motion cueing to provide an authentic learning environment. Coping and recovery skills are learned by pilots in an interactive experience to optimize training transfer to the aircraft. The result is a safer pilot with advanced risk management skills; a must for today's flight environment.
SPATIAL Disorientation
ETC's suite of spatial disorientation trainers optimize the elements of simulation fidelity including cockpit, visuals, flight model, and vestibular stimulation through continuous motion cueing to provide an authentic learning environment.
GYROLAB
ETC's GYROLAB series of advanced spatial disorientation trainers are designed to train aircrew, under safe conditions, to recognize and recover from phenomena encountered in flying high performance aircraft.
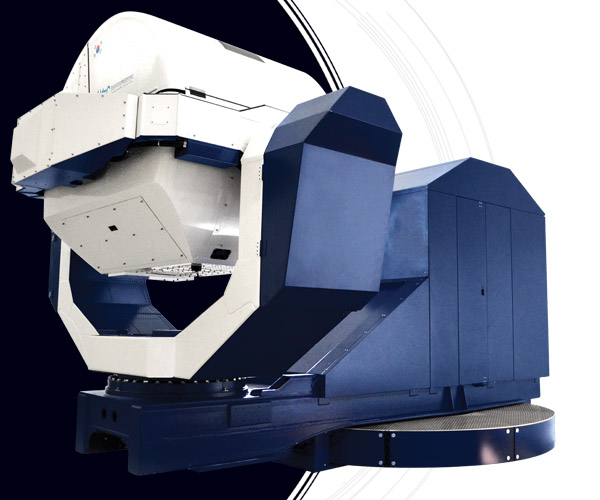
GL-4000
The GL-4000 is an advanced SD training platform that provides users with 360° of continuous and simultaneous motion in 4 axes of motion (planetary, pitch, roll and yaw) and up to 6 Gs of motion stimuli are generated in the planetary axis.
LEARN MORE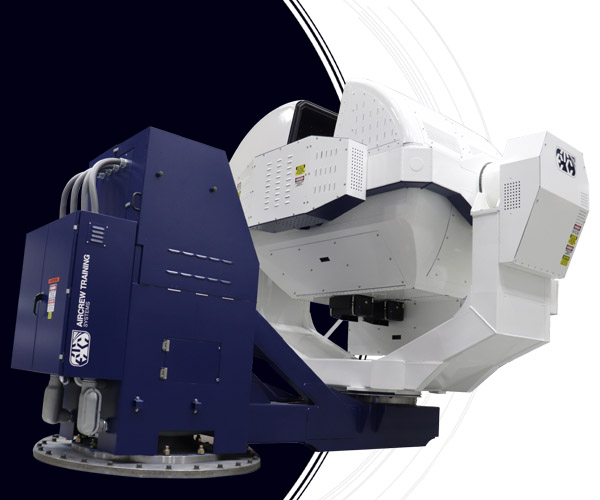
GL-1500
The GL-1500 is a single-seat motion platform that provides users with 360° of continuous and simultaneous motion in 4 axes of motion while generating up to 2.5 sustained Gz motion stimuli.
LEARN MORE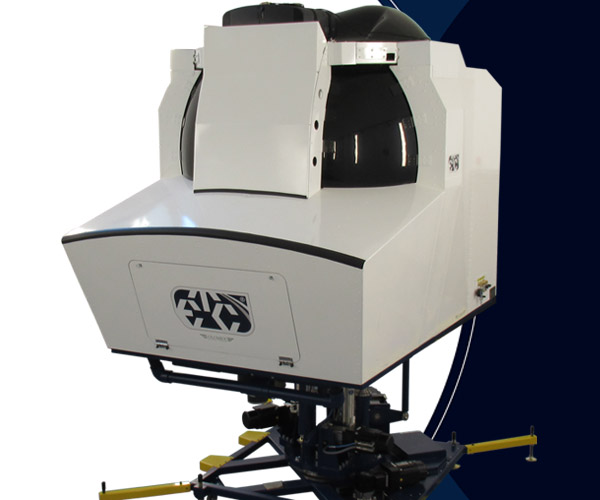
GYRO IPT-II
The GYRO IPT-II consistently duplicates situational awareness and spatial disorientation illusions felt in aircraft, but in a safe and controlled environment.
LEARN MORE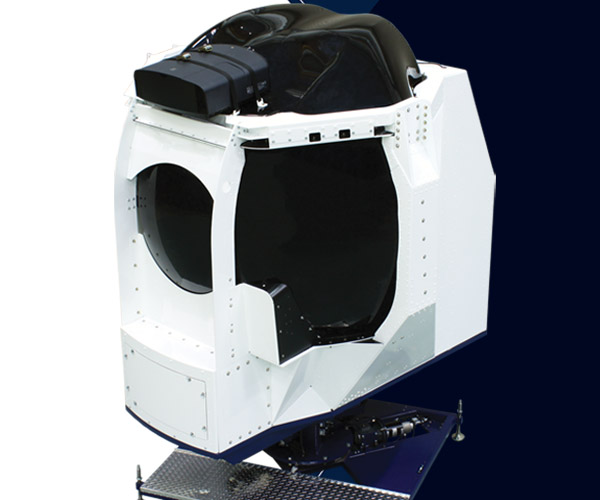
GAT-HELO
The GAT-HELO is our most cost-effective, transportable spatial disorientation simulator capable of delivering basic flight and spatial disorientation training.
LEARN MORE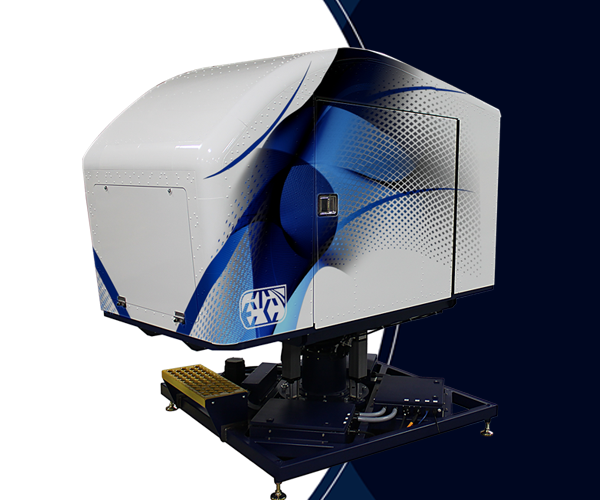
GAT-III
The GAT-III is a multifunctional general aviation and spatial disorientation trainer that supports a spectrum of pilot training, including spatial disorientation prevention and unusual attitude recovery.
LEARN MORERELATED ARTICLES

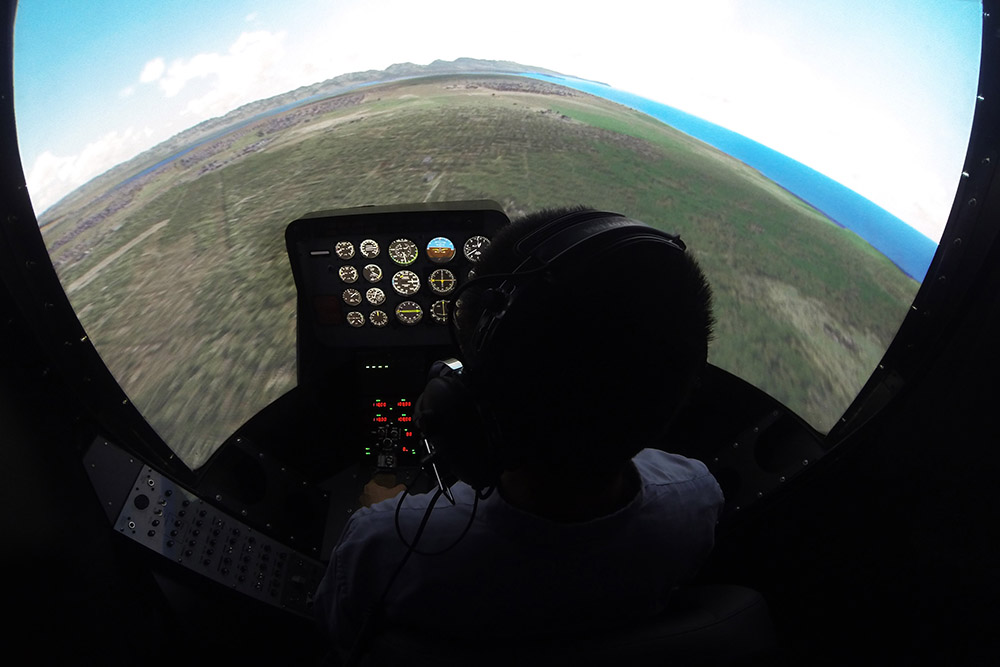
The GAT-Helo Trainer is a full-motion helicopter simulator combining basic flight training, instrument training, and degraded visual environment (DVE)/spatial disorientation (SD) training in one unique platform. The helicopter simulator features generic, light utility helicopter interactive controls with realistic, computer-generated instrumentation, and a full spectrum dome visual display.

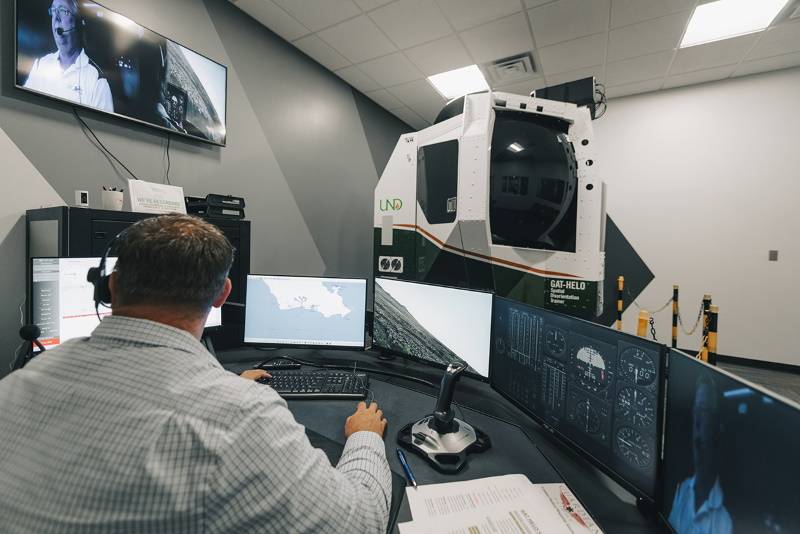
They're all trying to fix this problem of spatial disorientation in helicopters,” said Tom Zeidlik, director of aerospace physiology at UND. Once we get it, we will have the only one in existence outside of the military. Once it’s installed, Zeidlik said he anticipates an increase in the number of corporate helicopter pilots coming to UND for training.

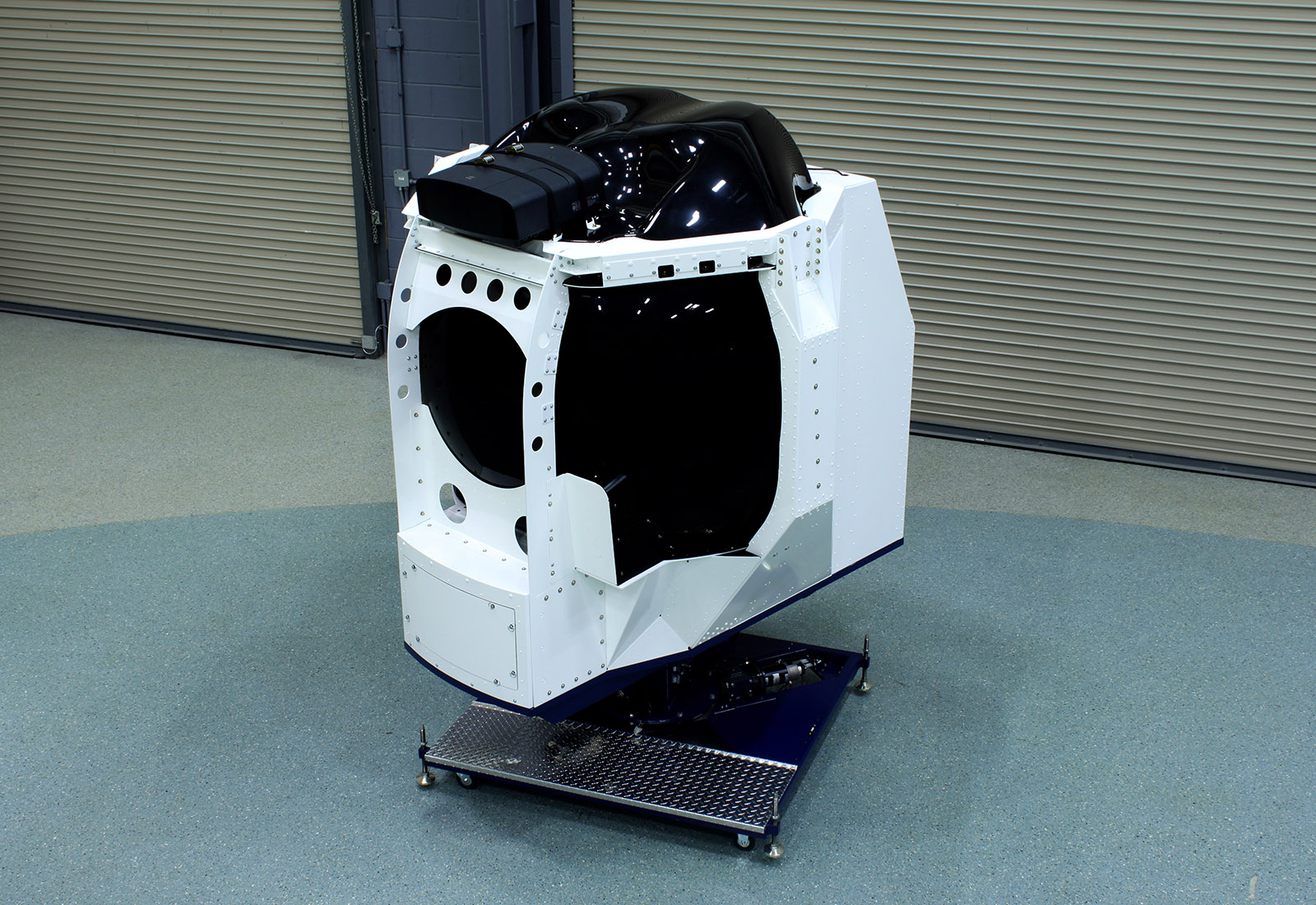
ETC's Aircrew Training Systems (“ATS”) unit, announced it was awarded a contract from the University of North Dakota’s John D. Odegard School of Aerospace Sciences (“UND”) for its GAT-HELO, Rotary Wing Spatial Disorientation (“SD”) Trainer. The GAT-HELO is ETC’s most cost-effective, helicopter simulator capable of delivering general flight and spatial disorientation training. The specialized GAT-HELO motion platform is designed to create in-flight illusions authentically and safely.
In this video, Noemi Distefano speaks to Glenn King, COO and director at the NASTAR Center, a division of training equipment manufacturer ETC, to obtain the company’s perspective on high-G and spatial disorientation training.
Valley Today visits University of North Dakota Aerospace to learn more about using the GAT-III for spatial disorientation training and research.
The Gyro Integrated Physiological Trainer, or Gyro IPT II was unveiled at Joint Base San Antonio-Randolph on Tuesday, June 7, 2016.

For the past year, the student pilots attending the 80th Flying Training Wing’s Euro-NATO Joint Jet Pilot Training program at Sheppard Air Force Base, Texas, have been using the GYRO Integrated Physiological Trainer II to get hands-on, realistic spatial disorientation training.

While Sheppard is the first to receive one, eventually each undergraduate pilot training base and Joint Base San Antonio-Randolph, Texas, will have one of the trainers by January 2016. At that point, all pilot training syllabi will include this valuable training for recognition and recovery from the dangers of spatial disorientation.